This condition affects mostly young adults, and the prevalence of the disease gradually decreases with age. Disc are protruding and occasionally tear into the spinal canal compressing the spinal cord, spinal nerves thus causing local and shooting pain.
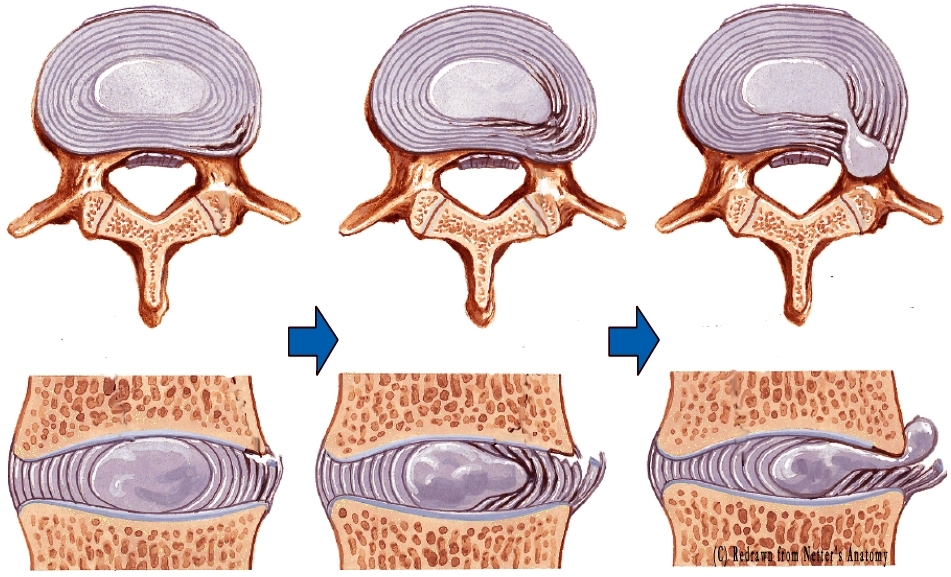
Two main parts of the intervertebral discs are the outer ring (annulus fibrosus) and the inner gelatinous material. (nucleus pulposus). The outer ring consists of fibrocartilage, while the inner material shows many similarities to the articular hyaline cartilage both in its biochemical and histological appearance. The function of the outer ring would be to keep the inner substance within the disc and resist the rotational and loading forces. The inner material functions as shock absorber for axial loads. Herniation is when the inner content of the disc protuberates through the fibrous ring and compresses nerves.
Prevalence
Herniation occurs mostly in young adults. May affect any level of the spine. In the cervical (neck) part of the spine it could provoke dull or shooting pain in the neck, shoulder, arm or even to the fingers. Similar changes in the lower lumbar segments cause low back pain, and shooting pain to the buttock and the lower limb, and the toes. Prevalence decreases with age as the water content of the disc is lower in elderly people, the intradiscal pressure is lower, and so the disc is less prone for herniation.
Complaints
Dull continuous pain may be present, pins and needles are common, and often sudden shooting pain develops, most often following heavy lifting or strenuous exercise. Shooting pain is usually affecting only one limb, and the pattern follows the dermatomes, thus only a narrow band of the skin is affected. Muscle weakness may occur. Severe weakness, difficulties in holding or expelling urine and/or waste is sign of emergency and immediate help is to be sought.
Usual protocol of examination
· Assessment of the gait and spinal curvatures, range of motion
· Stiffness of the paravertebral muscles.
· Neurological assessment
· Muscle strength measurement, assessing sensorium
· X-ray is usually not necessary, however, in prolonged complaints it may be taken, and in the presence of neurological deficit computer tomography (CT scan) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be required
Treatment options
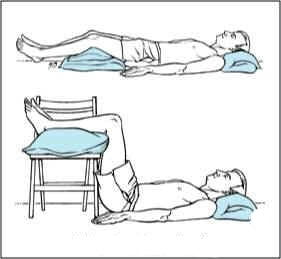
Acutely developed complaints are assessed and treated mostly with resting with specially elevated legs. Drug regime includes muscle relaxants, painkillers. After a short immobilization period of 2-3 days physiotherapist supervised mobilization is started, and usually in 2-4 weeks full recovery is expected.
In severe cases herniotomy, the removal of the herniated disc is necessary. In milder cases physiotherapy may be just as effective as surgery, however, if these painful periods recur surgery may be the only option
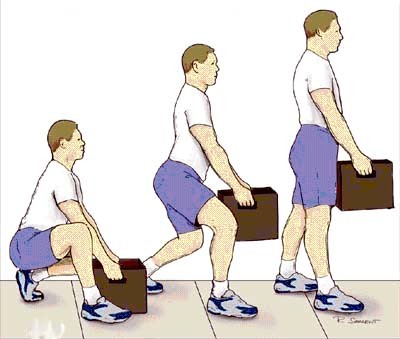
Prevention is priceless in these conditions, including ergonomical changes, education in the weight lifting, psychosocial balance and loosing weight if appropriate.