Principally, there are three types of cartilage tissue
1. Hyaline cartilage
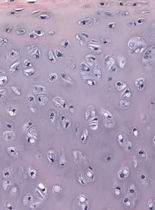
Hyaline means glass in Greek as its appearance resembles to the glass. Hyaline covers most of the bones in the joints, but is also present in the trachea and bronchi.2. Elastic cartilage
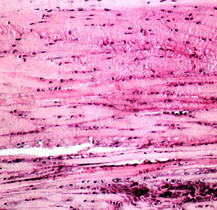
Elastic cartilage is present at the sites of large, deforming forces, as the ear, nose or the epiglottis.
3. Fibrocartilage
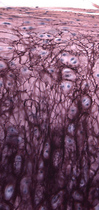
This specially strong but less resilient tissue is present at sites of large but not clearly compressive forces, such as the outer ring of the intervertebral disc (annulus fibrosus), or the menisci of the knee.
As articular surfaces are covered by hyaline cartilage we will describe hyaline cartilage in more details.
Hyaline cartilage
The cardinal function of articular cartilage is to evenly distribute the load between the joint surfaces, absorbs the shocks during physical activity, and it provides smooth gliding surfaces of low friction. Hyaline cartilage is composed of cells and intercellular matrix, containing collagen and proteoglycan fibers holding large amount of water around the fibers. (see Biochemistry). Cells The histological unit of hyaline is the chondron. The chondron contains 2-4 cells surrounded by highly basophilic PG containing cover. Cells are spherical or elliptic containing one or more nucleolus; cells in the deeper layers are spherical, however, towards the surface cells become flat.
Layers of cartilage
1. Superficial zone
Fibers are parallel with the surface, cells are flat
2. Transitional zone
Cells are spherical containing PG in abundance
3. Radial zone
All fibers run perpendicular to the surface. The thickest layer thus its main function is to sock absorb and to distribute the load evenly.
4. Calcification zone
Separates as well as connects the cartilage with the underlying subchondral bone.
Cartilage has no blood supply, is aneural and alymphatic. Due to this character cartilage is highly immunoprivilged. As the extracellular matrix is quite dense the lymphocytes and the antigen presenting cells and even the immunoglobulines can not reach cartilage cells during immune surveillance